System and surrounding areas
system-and-surrounding
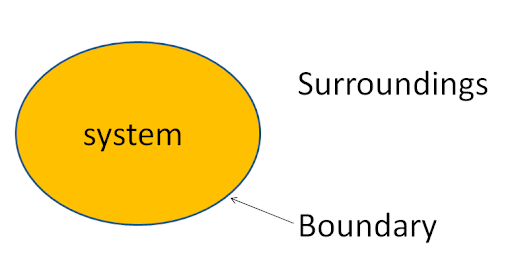
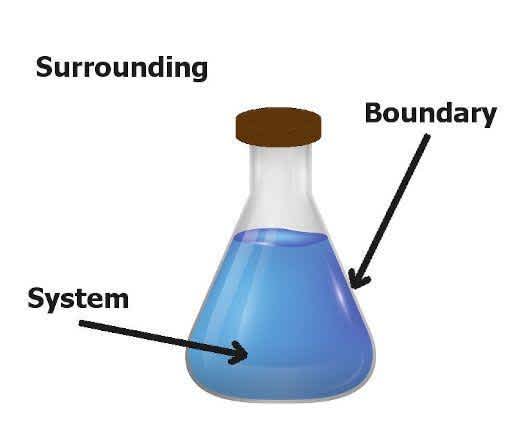
A thermodynamics system is the main portion of matter or radiation, confined in space by walls, which separate it from its surrounding. In other words, a system is a region that contains energy and matter that is separated from its surrounding wall or boundaries. The system boundary is a surface surrounding a system via which energy and mass may be in or out of the system. Surroundings mean everything that interchanges with the system.
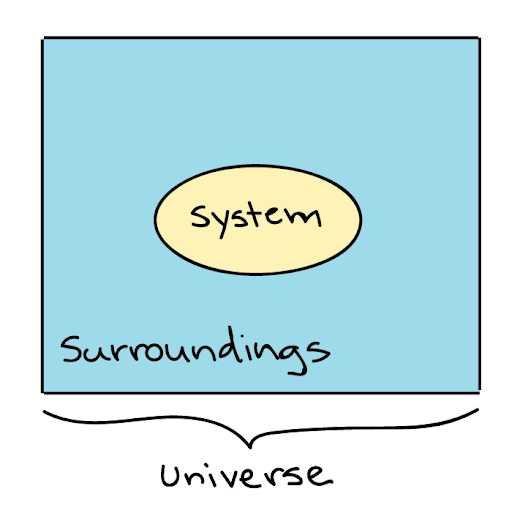
Universe= system + surrounding
Here, the path of the university chosen for thermodynamics is called a system, and the remaining portion of the University is surrounded.
A system consists of a clear amount of one or more substances and is separated from the surrounding boundary; it may be real or imaginary through which energy and matter can flow from the surrounding to the system or vice versa.
Open system
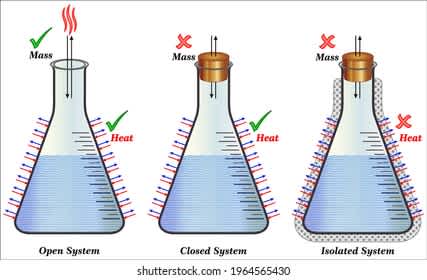
An open system is a system that interacts with the external and that interaction can take the shape of data, material transfer, or energy into or out of the system boundary. It is a system where energy and matter are often exchanged with their surroundings. As a difference to close systems the most genuine thermodynamics systems are open systems that exchange with surroundings. As they grow and improve living systems, they construct structures with greater internal energy from the nutrients they take. The matter and energy are easily exchanged between the system and its boundary. Simply this can be described by adding or subtracting matter or energy. On the other hand, energy exchange can be a little more complex because energy is transmitted frequently in multiple and different forms; transformations might occur throughout this process. Heat or energy is exchanged.
In thermodynamic, the energy exchange is defined as:
Potential Energy: It is energy stored in the object because of its relative position to other objects. You have more potential energy when you stand at the top of the stairwell as compared to at the bottom, as the force of gravity pulls you down, doing work in the process.
Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object in motion.
Thermal energy: It is the energy possessed within the object or system. This system presents internal energy in a state of equilibrium.
![open-closed-isolated]()
open-closed-isolated
The figure shows open, closed and isolated system
Close system
A closed system is a system that does not allow the exchange of matter but allows energy to be transferred. The heat can be transferred from the water to the stove. Heat is also transferred to the surroundings. Steam is not allowed to escape.
Example: Water bottle
In other words, it is a type of thermodynamic system where mass is protected within the boundaries or surroundings of the system, but energy is allowed to enter or exit the system freely. A closed system is one of the systems in which products or matter can't be entered or exited, yet which allows energy like heat or light to be transferred.
One type of particle atom or molecule, a closed system amounts to an invariable number of particles. Although, for systems that are going through a chemical reaction, there may be all sorts of molecules being generated and destroyed by the reaction process. In a close system, the fact that the system is expressed by stating that the total number of each elemental atom is protected, no matter what kind of molecule it may be a part of. Where thermodynamics equilibrium is required to simplify the situation the close system can be used.
Example of open and close system
Some examples of the open system:
The earth in this world is the system and space.
You can send a rocket to space and sunlight reaches the surface of the world.
An open cup of tea or coffee.
Boiling water.
A living organism is like a human.
Ecosystem, here energy entered in the form of sunlight and leaves in the form of heat.
Flowing water in the river.
A car engine that exchanges heat and matter.
And everything that has external interaction.
Some examples of a close system:
A pressure cooker, we cook food and receive energy that is heated and it does not allow gas to get out.
A Stirling engine receives thermal energy in this type of motor energy, the work done by the system is positive.
A solar thermal system captures the energy from the Sun and provides thermal energy to another system. Hence, the total mass remains constant.
The piston-cylinder internal engine is only a closed system, the piston-cylinder system is approximated by an ideal gas or an atomic gas.
Covered beaker of water.
A cup of coffee or tea with a lid on it.
Water bottle.
An airtight box or container.
Isolated system
An isolated system that can not exchange energy or matter outside the boundaries of the system. The system may be enclosed with immovable energy or mass to enter and exit. An isolated system performs the conversation law which means energy and mass stay the same. The idea of an isolated system can serve as a useful model for almost many real-world circumstances. It is a suitable value used in constructing mathematical formulas of certain natural phenomena; e.g., the planets in the Solar System, and the electron and proton in a hydrogen atom are often treated as isolated systems. A hydrogen atom will interact with electromagnetic waves from time to time and go to an excited state.
Some examples of an isolated system:
The physical universe is an example of an isolated system.
Combustion of glucose in a bomb unless some parameters take place.
A closed thermos bottle or a vacuum flask.
Surrounding
surroundings
Surroundings are everything around a system. For example, air on all sides of the cylinder with a piston. In the other words, the exchange of any system with an exacting system is called surrounding. Anything which is externally from the system will be known as surrounded. The system boundary will be divided by the surrounding. A system through which energy and mass might come in or out is the boundary in the closed surface surrounding.
Everything outside the system is the surroundings. Through the flow of heat, the system can exchange energy with its surroundings. We can also say that everything else that is not a system is surrounding. For example, if the system is in the building then everything outside the building is the surroundings. In easy words in a universe apart from the system everything is surrounding.
Example of surrounding
A car engine in which outside the cylinder, the piston, exhausting system, radiator, and air are surrounding.
The wall of the container or box or bottle is part of the surroundings.
Everything around the system is surrounding.
The water molecules surrounding the acid don't react so they are known as the surroundings.
Sign convention for thermodynamics quantities
In thermodynamics, the sign convention is that energy added to the system is normally used in the form of heat and is taken as positive and if the same that is added in the form of work is taken as negative. Although this is a common sign that all forms of energy added to a system as heat or work are positive. This also occurs in cycle analysis in which the absolute value is as energy transfer.
To use the sign convention for thermodynamics quantities, when Heat absorbed by the system is equal to q+(positive), Heat evolved by the system is equal to q-(negative), Work done on the system is equal to w+(positive) and Work done by the system is w− (negative). When volume increases in the system it does positive or negative work? Due to work done by the system the volume increases. That's why W is negative about using your notation. In another way, you can understand it when work is done on the system it would push the system inward and the volume is decreased.
The other way of using the formula is:
dU=dQ−dW
Here, U is internal energy, W is work and Q is heat to the system
dW=PdV
Therefore, dU=dQ−PdV
So dV(volume change) is positive, and dU (change in internal energy) is negative.
boundary
Conclusion
As you see above, there are basic terms and concepts in thermodynamics, and a deep understanding of the term system and surrounding with their types is an open, close, and isolated system with the help of examples in our daily life so that it is easy to understand the concept. In the last, there is a sign convention for thermodynamics quantities in which there is an understanding of positive and negative work in the system. Lastly, in the short surrounding is everything around the system and the system is the main portion of the universe.