Introduction:
A refrigerator is a business and residential equipment that consists of a heat pump that transfers heat from the inside to the outside environment, allowing the interior to be cooled to a temperature below room temperature.
Refrigeration is a common food preservation method used in this modern world. Because germs reproduce at a slower pace at lower temperatures, the refrigerator lessens the rate of deterioration. The temperature of a refrigerator is kept a few degrees above the freezing point of water.
Working Principle:
It entails taking heat from one place and transferring it to another. When you pass a low-temperature liquid near things you wish to cool, the heat from the objects is transferred to the liquid, which then evaporates and removes the heat.
In the refrigeration process, another principle comes into play. When two objects of different temperatures are nearby or come into physical touch, the hotter surface cools while the cooler body warms up. The second rule of thermodynamics describes this type of event.
How does Refrigerator work?
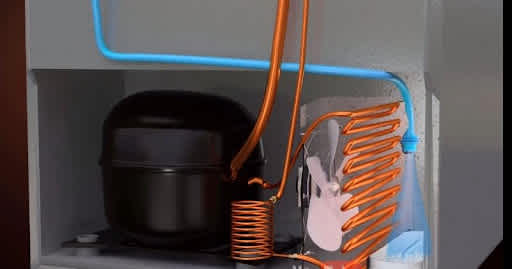
There are five fundamental components in the refrigeration cycleFluid Refrigerant, Compressor, Condenser Coils, Evaporator Coils; And Expansion Valve.
Fluid Refrigerant :
It is the liquid that keeps the refrigeration cycle running. It is also known as coolant. It is, in reality, a specifically designed chemical that can switch between being a hot gas and a cool liquid. Fluorocarbons, particularly CFCs. However, they are being phased out in favor of more environmentally friendly refrigerants such as ammonia, R-290, R-600A, and so on. Because of their toxicity, flammability, and the impact of CFC and HCFC refrigerants on ozone depletion, as well as the role of HFC refrigerants in climate change, refrigerants are extensively controlled.
Compressor:
The compressor's duty is to compress and regulate the flow of refrigerants. The compressor accepts low-pressure gas from the evaporator and turns it into high-pressure gas. The temperature rises as the gas are compressed and the pressure is increased.
Compressors can be positioned on the top or bottom of a refrigerator. Top-mounted compressors are ideal for dry storage locations where the floor might become dusty and coated in spilt materials. Bottom-mounted compressors are ideal for hot regions and line cook applications.
refrigerator-banner
Evaporator:
An evaporator in a refrigerator system's fundamental job is to extract heat from the water, air, and other things present in the refrigerator. Refrigerator evaporators function as heat exchangers, transferring heat from the material and allowing it to chill.
In the refrigerator system, two types of evaporators aid in the heat exchange process and keep your food fresh for a longer amount of time.
Forced Convection:
A forced convection refrigerator evaporator uses a pump or fan to drive the liquid that has to be cooled down over the evaporator.
Natural Convection:
A natural convection refrigerator evaporator aids in the natural cooling of the flow of liquid inside the refrigerator. Natural convection operates because the density of a cold and a heated liquid is different.

natural-convection
Condenser:
A condenser is one of the key operational components of a conventional refrigerator's cooling system. The condenser is usually found near the rear of the unit. However, it can also be found on the bottom or along one side. The condenser takes heat from the refrigerator's interior and sends it to the unit's outside. The temperature of the refrigerant decreases to condensation temperature when the heat is removed, and it changes state from vapor to liquid.
Expansion Valve:
The expansion valve relieves pressure on the liquid refrigerant in the evaporator, allowing it to expand or change state from liquid to vapor. An expansion valve, also known as a flow control mechanism, regulates the flow of liquid refrigerant into the evaporator. It's essentially a very little gadget that's sensitive to refrigerant temperature variations.

expansion-valve
The compressor compresses the refrigerant vapor, increasing its pressure, and pushes it into the refrigerator's coils on the exterior.
When the heated gas in the coils comes into contact with the kitchen's colder air temperature, it turns into a liquid.
The refrigerant, now in liquid form and under high pressure, cools as it flows into the coils inside the freezer and refrigerator.
The refrigerant absorbs the heat generated within the refrigerator and cools the air.
Finally, the refrigerant condenses into gas and returns to the compressor, where the cycle begins again.
Coefficient of Performance
The heat extracted from the cold reservoir Qcold divided by the work W done to remove the heat is the coefficient of performance, or COP, of a refrigerator.
When more heat Qcold can be removed from the interior of the refrigerator for a given amount of effort, it is called a refrigerator. We can rewrite the above equation using the first law of thermodynamics (Qcold + W = Qhot)
Efficiency of Refrigerator
The energy consumed per year for a certain size determines a refrigerator's efficiency. A refrigerator's efficiency is measured in volume chilled per unit of electric energy used each day. Electrical energy is measured in kilowatt-hours and volume is measured in cubic feet.
The ratio of a refrigeration machine's COP to the matching Carnot COP will indicate how excellent or poor the machine is. This is what I refer to as refrigeration efficiency.
efficiency-of-refrigerator
Laws of Refrigerator
1. When a fluid transitions from a liquid to a vapor state, it absorbs heat and releases it when it transitions back to a liquid form. 2. If the pressure remains constant, the temperature at which the transition of state happens remains constant.
3. Heat flows only from a body that is at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature.
4. States that energy is neither created nor destroyed but can be converted from one form to another
5. The work done by the compressor is converted into heat. The heat lost in the condenser is equal to the sum of the heat obtained in the evaporator and the work input in the compressor.
Reverse Heat Engine
The reverse heat engine is a device that works on the system to transfer energy from a lower temperature item to a higher temperature object.
Refrigerators are reverse heat engines that use an electric motor to push energy out of the refrigerator and into the surrounding environment. They take energy from one system and pump it into the surrounding region, which is at a greater temperature.
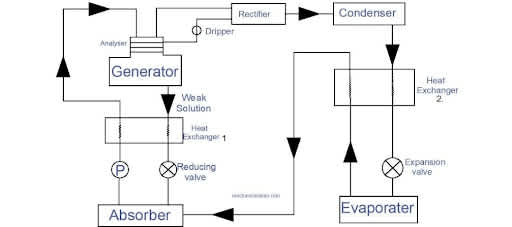
Vapor-absorption cycle
A Vapor absorption cycle is a mechanical vapor-compression cycle with a generator, absorber, and liquid pump replacing the compressor. The absorption cycle employs natural molecules like ammonia and water instead of ozone-depleting halocarbons and only a fraction of the electrical input.
A variety of working pairs can be used in a vapor absorption cycle. A refrigerant, usually ammonia or water, and a solution that absorbs the refrigerant make up the working pair.

vapor-absorption-cycle
Gas-cycle refrigeration
Refrigeration using the gas cycle is effectively a reversed Joule cycle also called the gas turbine cycle. The refrigerant used in these systems is gas, as the name implies. It works in a similar way to the vapor-compression cycle. The key difference is that an expander replaces the throttling valve.
The following describes the cycle:
Compression adiabatic.
Cooling under constant pressure.
Adiabatic expansion.
Heating at a constant pressure.
The gas cycle is less efficient than the vapor cycle for given evaporator and condenser temperatures because the gas does not accept and reject heat at a consistent temperature. The working fluid-air can be evacuated at T4 in gas-cycle systems, which are commonly employed in air conditioning applications. The air cooling of airplanes is a popular use. The compressed air is cooled via a heat exchanger before being expanded through a turbine. The turbine's power is utilized to power a fan that supplies cooling air for the heat exchanger. To provide the requisite cooling, the air is expelled into the cabin at T4.

gas-cycle-refrigeration
Applications of refrigerator/refrigeration
Refrigeration applications may be divided into four categories, each of which is equally important:
Processing, preserving and distributing food
Process and chemical industries
Other Special Applications
Processing, preserving and distributing food:
One of the most essential applications of refrigeration is food preservation. Food goods may be kept at lower temperatures for a long period, which is generally known. Refrigeration may be used to preserve both live and dead items for a longer period time.
Fruits and vegetables are examples of live goods, while fist, meat, and other dead items are examples of dead products.
Process and chemical industries:
In the petrochemical industry, for gas separation and liquefaction.
In many chemical industries, for the elimination of reaction heat.
In the pharmaceutical industry, for dehumidification of process air.
Other Special Applications :
Cold treatment of metals is used to increase dimensional accuracy, hardness, wear resistance, and tool life in precision components and cutting tools.
In construction, it's used to speed up the setting of concrete and to freeze wet soil to make excavation easier.
A Local anesthetic is used in surgery.
In isolated and rural places, for vaccine and pharmaceutical storage.
Conclusion
A refrigerator has two compartments: one for frozen products and the other for items that need to be kept cool but not frozen. It can dissipate all of the heat generated by the loads inside the compartments, resulting in a cool and long-lasting environment. It is suited for use in the culinary and medical industries.
The refrigerator's innovation has a worldwide influence. It altered people's lifestyles by obliterating several customs. Meat, fish, and fresh fruits can now be carried to practically any location, which has enhanced people's quality of life. As a result, one of the most essential technologies that have become an intrinsic part of daily life is refrigeration.
Even without decaying, the inconsistent ways of keeping food would present difficulties for flavor and health, as some meals needed the usage of chemicals that were particularly harmful over time.