Many devices need rotating parts for their operation. One such device used is an electric motor. An electric motor is a rotating device. It plays a role in energy conversion. The theories of electric motors are studied in physics.
The electric motor is a widely used instrument. It is used in day-to-day life. The electric motor is useful in converting one form of energy to another. The electric motor is used in vehicles, devices, etc. It works on the principle of electromagnetism. This article will help you understand the working, construction, etc. of an electric motor.
What is an electric motor?
An electric motor is an instrument that converts energy. The electric motor is a type of rotating device. It converts the electrical form of energy into a mechanical one. It operates according to the principle of electromagnetism. It operates because of the interaction between the magnetic field of the motor. The magnetic field interacts with the electric current in the winding wires. This interaction produces force in the form of torque. This torque is applied to the shaft of the motor.
Direct current or Alternating current is used to power the electric motor. Direct current is transferred by batteries or rectifiers. Alternating current is transferred by inverters, electrical generators, and power grids. Electric motors are classified on basis of many factors. Like the type of power source, applications, etc.
Principle of electric motor
Every instrument has a different principle. Principle describes the theory on which the instrument work. The electric motor also has a defined principle. An electric motor works on the principle that when a current is passed through a rectangular coil placed in a magnetic field, a force is applied to the coil. This force is responsible for the continuous rotation of the motor.
Because of this rotation energy conversion takes place. In simple words, the principle of the electric motor is relayed to a current-carrying conductor. This current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field. This current-carrying conductor is placed in the perpendicular direction of the magnetic field. Due to this, it experiences the force.
Construction of an electric motor
Every device has a unique construction. Understanding the construction is necessary. Here is an explanation of the construction of an electric motor.
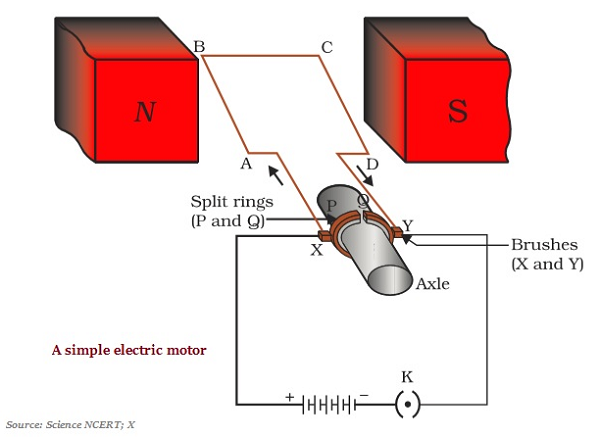
Construction of an electric motor
It has a rectangular coil of wire ABCD.
It has got a strong horseshoe magnet. The coil ABCD is placed perpendicular to this magnet.
The ends of the coil ABCD are connected to split rings P and Q. These split rings play the role of the commutator. It helps reverse the direction of the current flow.
The inners part of the split rings is insulated. It is attached to the axle. The axle is free to rotate.
The external side of the conducting edges of the split rings is connected with the stationary brushes. These brushes X and Y are connected with the battery. This completes the circuit.
This is the overall construction of an electric motor.
Parts of an electric motor
An electric motor comprises many parts. These parts are essential for the smooth working of the motor. Here is a description of the major parts of an electric motor.
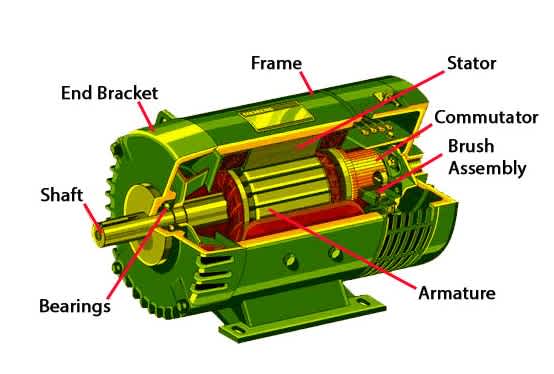
Parts of an electric motor
Rotor: It is a moving part of the motor. Its role is to rotate the shaft of the motor. This rotation in the shaft produces mechanical power. The rotar also comprises a conductor. This conductor carries currents. It also helps in communicating with the magnetic field present in the stator.
Bearings: Bearings are used to provide support to the rotator. This is essential to activate the axis of the rotor. With the help of these, the shaft of the motor expands. It extends up to the load of the motor.
Stator: This is an inactive part of the electromagnetic circuit of the motor. It comprises permanent magnet and windings. The stator can be made of thin metal sheets. They are called laminations. They help reduce energy loss.
Windings: Wires laid inside the coil of an electric motor are called windings. They are usually wrapped around a flexible iron magnetic core. This makes magnet tic poles when the current is supplied.
These were all the important parts and their uses in an electric motor.
Working of an electric motor
The electric motor as mentioned is a rotating device. The working of an electric motor explains its mechanism. Here are some steps which explain the working of electric motor.
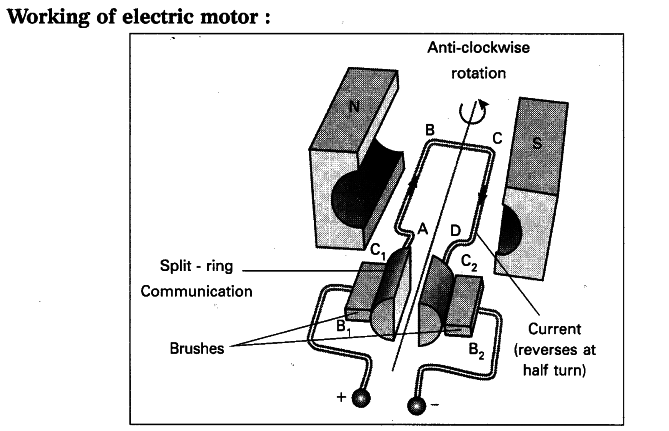
Working of an electric motor
When the battery of the motor is switched on current flows in it. Current flows via coil AB from A to B. During this, the magnetic field direction is North to South. About Flemings Left-Hand rule, a force acts downwards on AB. Similar to this an upward force is applied on CD. Due to this, the coil rotates. AB moves down and CD moves up.
Now both coils AB and CD are at interchanged positions. Now the flow of current is from C to D. And the magnetic field direction is from North to South. Coil CD receives an upward force and it moves upwards. Coil AB moves downwards. So both the coils do half rotations.
An electric motor requires full rotation to operate. To obtain this the direction of the current flow is changed. The direction of the current is changed using a commutator. A commutator has two split rings. Brushes are also attached to its circuit.
As the rotation of the coil begins the rings also spin. Once the coil becomes parallel to the magnetic field the brushes touch the gap between the rings. Due to this the circuit breaks.
Because of inertia, the ring continues to move. The opposite end of the ring gets connected to the positive end of the wire.
Split ring P and Q are attached to coil CD and AB respectively. Due to this the direction of current is reversed in the circuit.
Coil CD is on the left and coil AB to the right. Current in coil CD is reversed. Now the current flows from D to C. An upward force acts on AB and a downwards force on CD. This keeps the coil rotates.
This reversion of electric current takes place after each half rotation. This keeps the coil rotating till the battery is turned off.
This is the detailed working of an electric motor.
Benefits of an electric motor
Electrical motor serves many advantages. It is better than other energy-converting devices. There are many benefits of using an electric motor. Some of them are as follows:
The primary cost of an electric motor is quite low. It is better than engines using fossil fuels.
The electric motor has got various working parts. Due to this, the electric motor has a longer lifespan.
The motor requires less Maintainance. An electric motor has an average capacity of 30,000 hrs.
The electric motor has got an automatic control. It eases the controls and has automatic start and stop functions. Also, electric motors are very efficient.
They do not make use of fossil fuels. This is because they do not need engine oil.
These are various advantages of an electric motor. Due to these advantages, it is a widely used instrument for energy conversion.
Application of an Electric Motor
The electric motor is used widely. It has got many applications. These applications describe the use of an electric motor., Electric motors are an essential part of many instruments. It has many applications. Some of them are:
The electric motor is used in blowers, machine tools, power tools, pumps, and turbines. It is also used in rotating devices like compressors, rolling mills, fans, ships, movers, etc.

Applications of an electric motor
The electric motor is also a must-have component in many devices. These include heating and cooling equipment, various home devices, and also motor vehicles.
These are a few applications of an electric motor.
Conclusion:
The electric motor is a widely used instrument. Its primary purpose is energy conversions. It is efficient in converting electrical energy to a mechanical form of energy. Its functioning can be explained by the principles of electromagnetism.
It has various parts and unique constructions. It’s cheaper and more efficient than any other energy-converting instrument. It has a wide range of applications. The overall electric motor is an efficient device.