History
Before the development of the gasoline-powered engine, mechanical transportation was fueled by steam. A number of scientists tried their best to hatch force by heating water to generate power. Leonardo Da Vinci was one of them; he designed a steam-powered cannon which was widely known as the Architonnerre during the 15th century. Until the mid - 1600s there were no such working motors that came up. This was the era where a number of inventors tested and developed piston systems as well as water pumps, that led the road to a commercial steam engine. Since then, the commercial steam engine was made possible through three main figures; Thomas Slavary (1650-1715), Thomas Newcomen (1663-1729), James watt (1736-1819).
The steam engine was built between 1942-1950 and was operated till 1988. Thomas Slavary discovered the first crude steam engine based on the pressure cooker of 1679 or Denis Papin’s Digester. Later on, Thomas Slavary worked with Thomas Newcomen on the atmospheric steam engine. The steam engine was the first-ever commercially successful invention that could transmit a huge amount of power to other machines, it was first developed by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, along with John Calley built their first engine on top of a water-filled mine shaft and used it to pump water out of the mines. The engine was further modified by James Watt, who made a very crucial improvement, the spent steam was removed to a separate vessel for liquefaction, this change in the engine drastically improved the functioning as the amount of work obtained per unit of fuel consumed was much higher. The invention of the stationary steam engine powered the faces of big factories during the industrial revolution in the 19th century.
The invention ousted steam locomotives that operated on the railways and the sails for ships on paddle steamers. During the 20th century, the reciprocating piston-type steam engines were the assertive source of power, but it was gradually replaced for commercial usage by the advances in the model of electric motors and internal combustion engines. Further due to low cost, higher efficiency, and higher operating speed the steam turbines were replaced by reciprocating engines in power generation.
What is a steam engine?
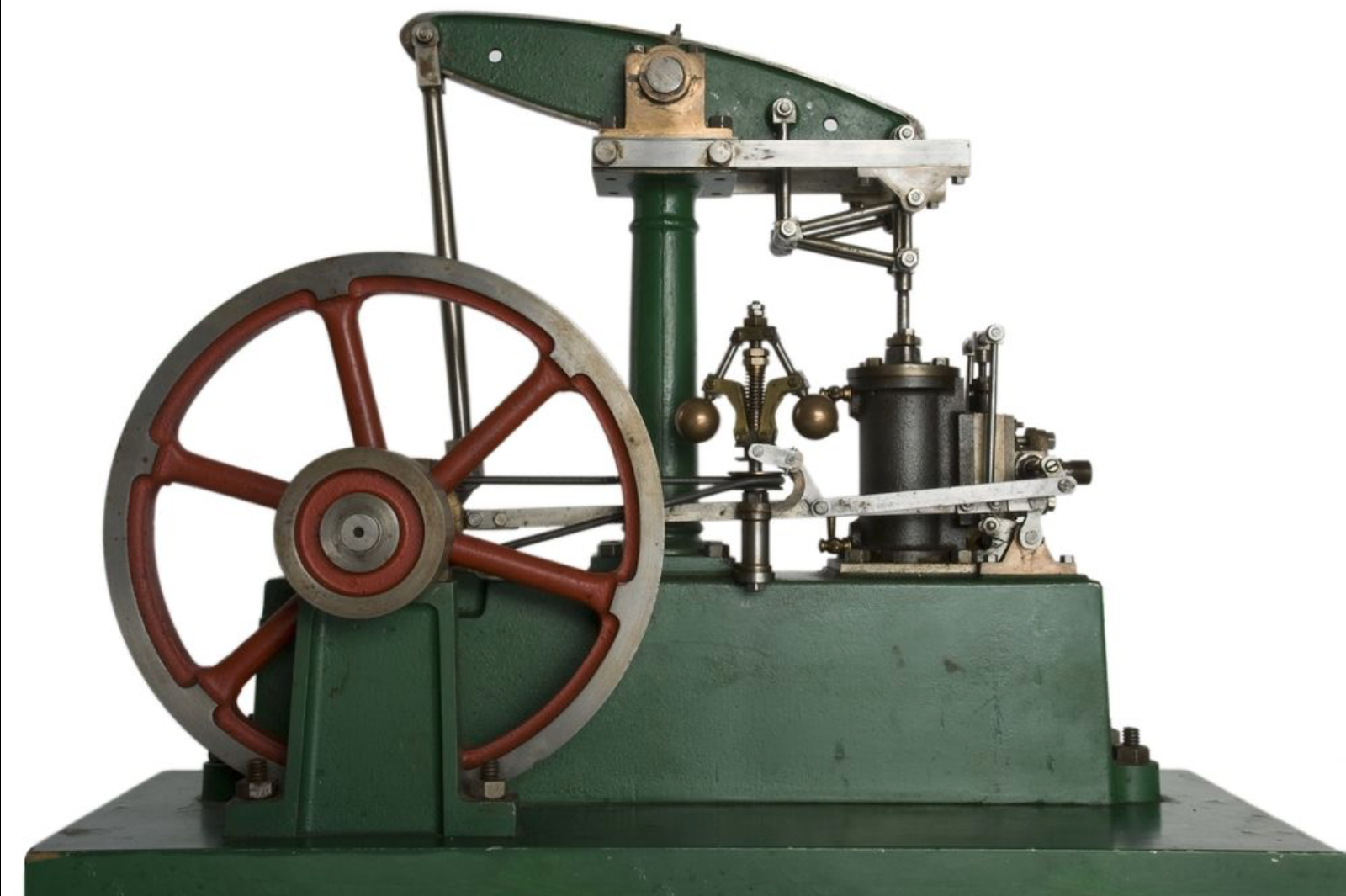

basic steam engine
A steam engine is a heat energy-producing station that works machine-like, handling strength as allure of busy fluid. The turbine uses psychic power provoked by strength pressure to push an instrument backward and forward inside a cylinder. This aggressive force may translate, by a joining bar and a regulating wheel, into a whirling force for work. The term “steam engine” is mainly used only to equal transformers as just described, and not to energy transformers or steam turbines. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the active fluid is terminated from the combustion output. The paragon thermodynamic cycle used to resolve this process is named the Rankine cycle.
Types of steam engine
A number of scientists have classified the steam engine on various bases. But the following are the main types of the steam engine, namely;
1. According to the position of the cylinder
Vertical steam engine
Horizontal steam engine
2. According to the type of exhaust
Condensing steam engine
Non-condensing steam engine
3. According to the number of working strokes
Single-acting steam engine
Double-acting steam engine
4. According to the expansion of steam in an engine cylinder
Simple steam engine
Compound steam engine
5. According to the speed of the crankshaft
Slow speed steam engine
Medium speed steam engine
High-speed steam engine
6. According to the method of governing employed
Throttling steam engine
Automatic cut off the steam engine
Different parts of a steam engine
All the parts of a steam engine concede possibility be widely detached into two types is the fixed or stationary parts and mobile or moving parts, even though a steam turbine resides of many parts both the fixed and the moving parts, still the following are the main parts of a steam engine;
D-Slide Valve
Cylinder
Crankshaft
Piston
Cross-head
Piston Rod
Flywheel
Eccentric
Steam chest
Eccentric Rod and Valve Rod
Intel and Exhaust Parts
Frame
Connecting Rod
Governor
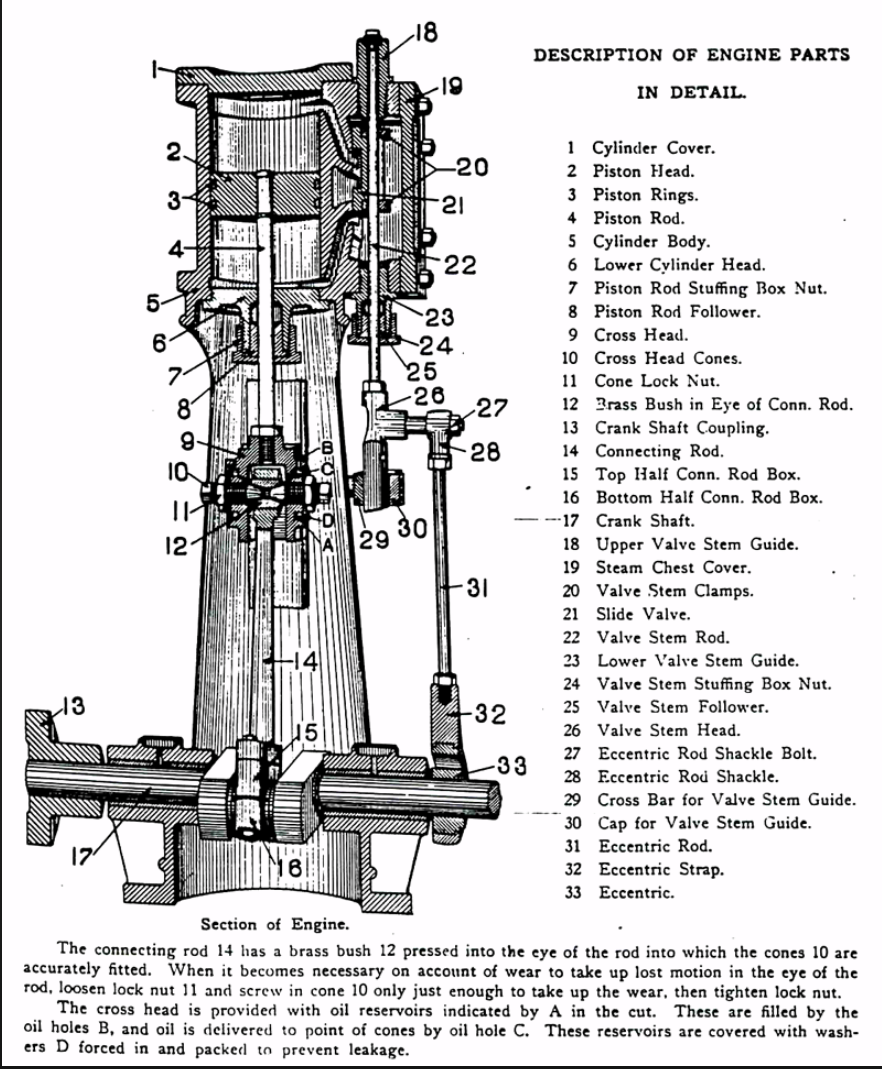
parts of steam engine
How does a steam engine work?
In a steam engine, new energy, customarily provided by a furnace expands under time pressure, and indiscriminate the heat energy, and it is then convinced into work. The residue of the heat can grant permission to escape or for maximum engine adaptability, the steam may be compressed in different appliances, a condenser, at relatively reduced temperature and pressure. For extreme adeptness, the steam must abort an off-course hotness range that is suitable for its inflation inside the engine. An ultimate effective performance especially, the greatest competition output of combined connection to heat provided is protected by utilizing a low condenser and an extreme furnace pressure.

how steam engine works?
The steam can be further heated, evading it through a superheater on the way from the heater to the diesel. A low superheater is a group of parallel pipes accompanying their surface unprotected to the new smoke in the boiler furnace. By way of superheaters, the steam can be heated above the hotness at which it is created by boiling water. In an alternating motor, the piston and cylinder type of steam turbine, energy under time pressure is permitted into the cylinder by a valve system. As the steam expands, it pushes the piston, which is ordinarily affiliated to a crank on a flywheel to produce a whirligig or a rotatory motion. In the double-acting engine, steam from the metal pot is permitted intermittently for each side of the piston.
In a natural steam engine, growth of the energy takes place in a singular barrel, whereas in the compound engine there are two or more cylinders of growing magnitude for better growth of the steam and greater adeptness, the first and minimal piston is conducted by the beginning, eloquent energy and the second by the lower-pressure steam drained from the first. In the steam engine, energy is dismissed at extreme speed through nozzles and therefore slows through an order of fixed and mobile blades, including a rotor to move at extreme speeds. Steam turbines are more condensed and regularly permit higher heat and better growth percentages than alternative energy generators. The generator is the universal method used to produce big qualities of magnetic competence alongside energy.
What is a steam engine used for?
The steam engine has had a variety of uses over the years. However, the following have been the most common throughout history:
Railway transport
Industrial
Water pumping
Marine transport
Generation of electricity
Steam engines have been utilized to power a variety of applications since the early 18th century. The steam engine was initially employed as a piston pump. Reciprocal engines appeared later, around the 1780s. This sort of external combustion engine was first utilized in factories and industries. The usage of steam engines in transportations began later.
Application of steam engine
Steam engines were used in all sorts of applications, it also included ;
Locomotives
Mines
Steamboats
Factories
Why were steam engines important for the industrial revolution?
During the industrial revolution, the steam engine was crucial. Steam engines were used to power the machines. Machines were driven by reversing river water wheels powered by river water turning wheels that ran machines during their use in the pre-Steam era. Machines could be created anywhere on the earth during the steam era. Steam power quickly surpassed that of water. It played a critical role as the system’s principal power source. The factory’s engine is running near the rivers. Furthermore, many manufacturers avoided constructing factories near bodies of water.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a steam engine
Advantages of steam turbines ;
The engines can be used where there are no other sources of power available.
The engine and the boiler can be placed apart.
The engine can be condensed into the water so that it can be used again.
A variety of fuels can be used to generate steam in a boiler.
It is compared to internal combustion engines.
The possibilities of combination are really great and varied, from ecological to non-ecological steam.
It has high torque. So there's no need to change gears.
It can work at high altitudes.
Disadvantages of steam turbines;
Modern engines are very compact as compared to steam engines.
In comparison to modern engines steam engines take a longer duration of time to start.
As compared to modern engines they cover more floor area.
They are less efficient, they have an efficiency of 10-15%, whereas modern diesel engines are near 27 and 45% efficient.
A larger engine crew is needed.
Need for copious amounts of water, which further requires constant refilling.
Requires high maintenance.
The engines are not able to be used bidirectionally like diesel-electrics.
Conclusion
Steam engines supplied convenient marketing, living, manufacturing, working, and specialty capacities without causing people to be concerned. Today, steam engines contribute to the health and wellbeing of many people through the construction of buildings and factories throughout cities and towns. After the steam locomotives began supplying faster and more efficient freight for us to and fro, transportation altered. We have the ability to establish new sectors and shape our present landscape into what we know and love today. Steam locomotives were instrumental in bringing the industrial revolution to many countries throughout the world.
